Sampling New Zealand’s (Amazing) Geology
New Zealand’s landscape can make just about anybody appreciate geology. Its glaciated peaks, its coastline –that ranges from ragged cliffs to sandy beaches to glacial fjords– its active volcanoes… they all work together to shout “Earth Science!” With that in mind, here’s some basics of New Zealand’s amazing geology, followed by some geological highlights of my trip of January and early February, 2018.
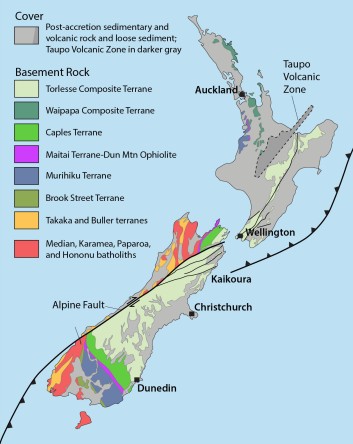
Map of New Zealand, showing accreted terranes in colors and cover assemblage in gray. (Compiled mostly from Graham, 2015)
North and South Island Bedrock The different colors on this map show New Zealand’s basement rock, named so because it forms the lowest known bedrock foundation of any given area. The basement tells stories of New Zealand’s deep past, from about 500-100 million years ago. Individual colors signify different terranes, accreted (added) one-by-one through plate motions to the edge of what was then the supercontinent Gondwana. They mostly consist of sedimentary and metamorphosed sedimentary rock, although the narrow belt of purple-colored Dun Mountain Ophiolite formed as oceanic lithosphere, and the red-colored areas consist of granitic igneous rock, some of which has been metamorphosed to gneiss.
Gray indicates the younger cover rock, formed after accretion of the terranes. Consisting of a wide range of sedimentary and volcanic rocks, as well as recently deposited sediment, it’s just as interesting and variable as the terranes. Because it includes volcanoes, it’s largely the cover that gives the North Island its distinctive flair. By contrast, the South Island consists largely of uplifted basement rock, much of which has been –and still is—glaciated. All those long deep lakes, such as Lakes Wanaka and Tekapo, were carved by glaciers and are now floored with their deposits of till.
Those differences exist largely because the North and South Islands occupy different plate tectonic settings. The North Island sits over a subduction zone, so it hosts an active Read more…
